What is an antioxidant?
 Antioxidant Rich Foods ... from Rainbow Colors of Fruits and Vegetables
Antioxidant Rich Foods ... from Rainbow Colors of Fruits and VegetablesIs it a Vitamin?
Is it a Mineral?
Is it an Enzyme?
It cannot be classified in the convention above, simply because it’s all of the above and more.
It is classified by what it does – that is, its role in countering the oxidation process. Hence, “anti” and “oxidant”, a class of its own!
Oxidation damages cells, nutrients and blood lipids. Antioxidants counter the damages caused, and can also repair the damages done.
P.S. - Just hold that thought for a moment on “oxidation process” which I shall explain on another page (check out “Free Radicals and Oxidation”).
Where do antioxidants come from?
It then begs the next question, where can we find it or them?
While antioxidants have been called the 21st Century herbal remedies or natural medicine, antioxidants can be found:
- naturally in the body
> some can be produced by the body
> and where lacking in production by the body, needs to be replenished through intake of foods and, where lacking from foods (for whatever reasons), through intake of supplements
And,
- naturally, in many foods (for the purposes of this classification, we shall include “water” here as well)
So, really, antioxidants have always been around ... long before 21st century, and have been used as herbal remedies and natural medicine for a long time, long before 21st century.
 Foods High in Antioxidants - Antioxidants Galore!!!
Foods High in Antioxidants - Antioxidants Galore!!!Classification within the Antioxidant Family
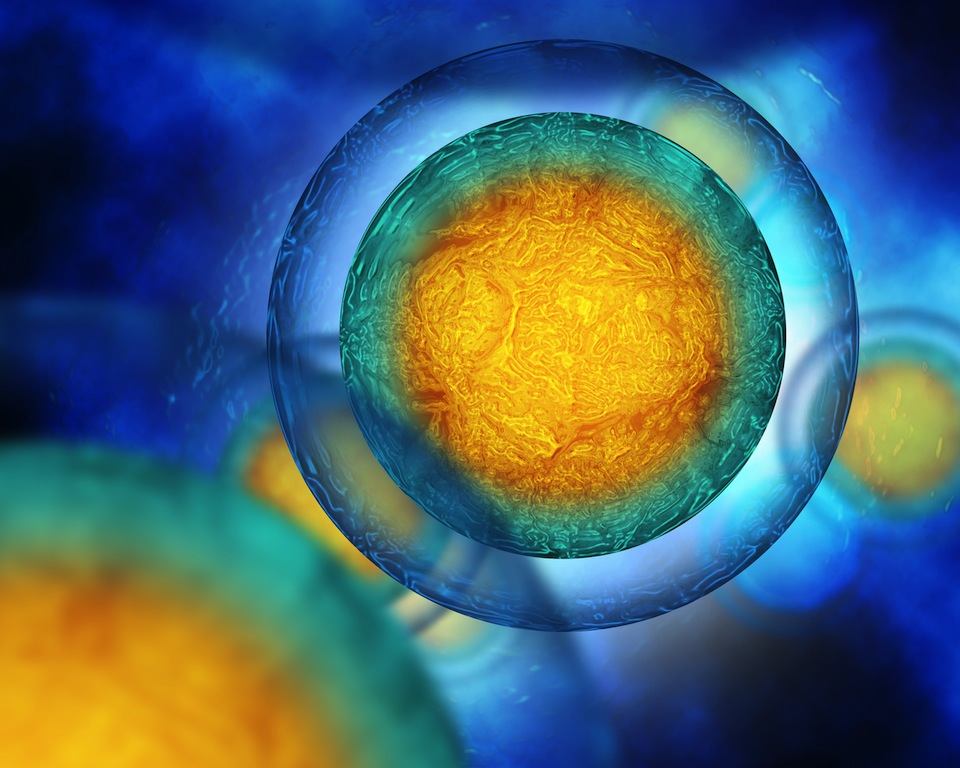
While in the bigger world of nutrients et all, it is defined by the role it plays in the cellular processes, but within the Antioxidant Family, they can be classified as/grouped as follows:
- Water-soluble
- Fat-soluble
- Both water-soluble and fat-soluble
This is important because it determines where different antioxidants can be utilized by the cells:
- within the cells or,
- by the cell membranes or,
- the cells' surrounding (such as, blood lipids)
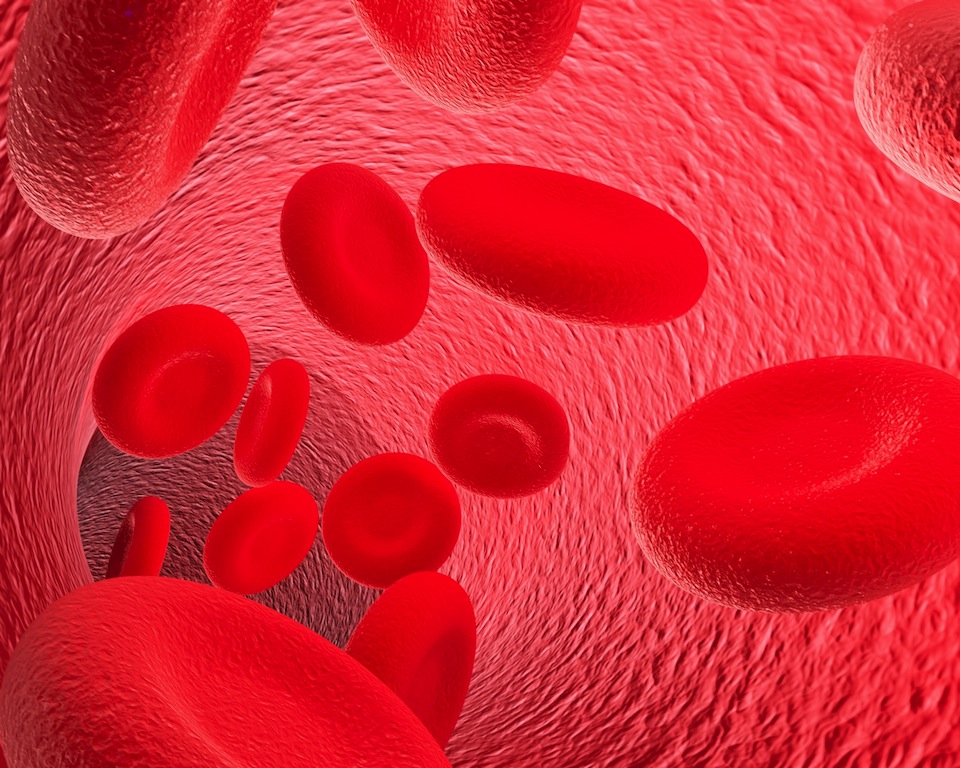 Blood plasma
Blood plasmaWater-soluble
antioxidants work their magic on the blood plasma surrounding the cells, since they are not able to penetrate the cell membranes, which, generally speaking, are made of lipids (i.e. fats) (plus a few other organic materials, technically speaking).
 Cell, Membrane and Nucleus
Cell, Membrane and NucleusFat-soluble ones work their magic on the cell membrane, which is made of mainly fats and lipids.
While the ones that are both water and fat-soluble, can work their magic on the cell membranes, as well as penetrating the cells to work on the inside of the cells; the inside of the cells contain water.
They are also sorted by the Nutrient Families they belong to, such as, Antioxidant-:
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Protein (Amino Acids)
- Enzymes and CoEnzymes
- Phytonutrients/Phytochemicals
o Carotenoids
o Ellagic acid
o Flavonoids
o Resveratrol
o Glucosinolates
o Phyoestrogens
- Antioxidants Other – including water
Side Note: This categorization is not universal. I have adopted what I think makes sense from a “lay” perspective, to aid understanding and for ease of referencing.
Antioxidants and Wellness

In broad terms, diseases can be categorized into:
- Degenerative diseases - defined as diseases brought on by wear and tear, through use and/or abuse of the body over time.
- Infectious diseases - diseases brought on by germs, bacteria, fungi, parasites, virus, and the like.
"Abuse the body?" I can hear some say “No way! I exercise and I feed it well!”. However, in today’s environment, the abuse can happen whether intentionally or not.


Our body is constantly exposed to high level of toxins, either through:
- Physiological factors, such as:
o Smoking
o Taking drugs or over medicating
o Living in a polluted environment
o
Consuming
foods that are toxic to the body – such as, unnatural food additives, and hormones
and steroids fed to animals (through consumption of their meat, and the animals' by-products)
o Drinking contaminated water (chlorinated and fluoridated water?)
o Radiation exposure (sunlight and Wi-Fi everywhere?)
o Over exercising
o Not consuming enough nutrients, leading to stress on the body

- Or, emotional factors, such as:
o Stress
o Anxiety
o Grieve
- And, even biological factors, most of which we can’t control, such as:
o Biological oxidation - our cells making energy so that we can function
o
Inflammation
in the body
o Even the process of countering oxidative stress produces more oxidative stress, but usually creates a lesser potent toxin, which needless to say, needs to be removed from the body.
 Degeneration: Cancer
Degeneration: Cancer Degeneration: Arthritis
Degeneration: ArthritisThese uses and abuses cause high oxidative stress in our bodies, and which in turn encourages degenerative diseases.
 Super Hero: Antioxidant
Super Hero: AntioxidantAntioxidants help us fight the degenerative diseases by:
- countering these oxidative stress
- and repairing any damages.
It can also help us to counter infectious diseases … indirectly. Here, antioxidants help us to build healthy cells and improve our immune system to counter germ (and virus /parasite/fungi/etc.) warfare.
We Are the Master of Our Body
We are a collection of our cells. Cellular health is important as we grow from our cells. Therefore, in simplistic terms, healthy cells make healthy bodies.
Hence, health begins at the smallest unit of us – our cells!
(Ok ... technically, we can go into smaller units, to atoms and DNA; but let's just stay with "cells", for simplicity's sake, otherwise we will need to get pretty technical with chemicals terms and all)
We are a collection of over a trillion cells. We are the Master (and the caretaker) of these cells who work so hard for us. Although there are a trillion of them, the good news is that we do not need to attend to each of them individually – it would be humanly impossible!
However, we need to help them, so that they can best perform their job in keeping us healthy.
How do we that?
We need to :
- Feed
the cells well – ensure required nutrients are supplied and, at the proper/right/correct amounts.
- Ensure toxins are removed from them (detox)
- Provide good environment for them to thrive in
How can antioxidants provide these? Well, antioxidants :
- are nutrients
- they remove toxins from the cells and their environment
- and thus, keep cells healthy and provide a good environment for cells to thrive in
If you like, they are an all-in-one answer to the 3 things needed to promote healthy cells in our body.
Specifically, How Do Antioxidants Work?
Briefly introducing free radicals ... Free radicals are the culprits that cause the oxidation process. In technical terms, they are molecules (or atoms or ions) short of one electron, which turns a perfectly harmless molecule (or atom or ion) into an “enemy” of our cells.
A bit like “Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde”- same person (molecule/atom/ion) but two personalities – one good and one evil. But unlike Mr. Hyde (the evil one), some free radicals are required by our body. (Interesting? …)
(Check out “Free Radicals and Oxidation” for more detailed understanding)
A very common example is an element that exist within our bodies (as you are reading this) … is oxygen! Oxygen molecules, which our body needs, once they are short of an electron, turns into perpetrator of our cells, the nutrients and the lipids.
So, how do antioxidants work ?
2 Ways :
I) Directly working on the free radicals - DIRECT Antioxidant effect.
Within this category, there are 2 ways in which the antioxidant work to neutralize the free radicals.
1) Preventative
- Stops the oxidative process before it can began. Almost like a immediate arrest of the free radicals before it can even begin its destructive moves.
> Such as, the antioxidant enzymes (produced by the body) or hydrogen from hydrogen enriched water.
2) Chain Breaking
- Here, they act generously towards the free radicals by donating their electrons to these poor chaps. Unfortunately, their generosity turns them into free radicals – yes, they become “Mr. Hyde” but of a lesser potency.
- Then
comes along other antioxidants to the rescue, and donate their electrons to
these “Mr. Hyde” antioxidants-turn-free-radicals. And in turn, they, too, become “Mr. Hyde”, but of a
lesser potency still.
- And this cycle continues, until the free radical potency becomes negligible.
- In the meantime, the “rescued” antioxidants can become themselves again, and be the very Nutrient they once were — maybe a little less potent but still valuable to the cells.
And so, in the antioxidant world, they need to work together. It’s a "community spirit" type of nutrient, if you like.
II) INDIRECT Antioxidant effect - where they induce or help produce the antioxidants. However, they may or may not also have direct effects as well.
- examples of Indirect antioxidants are melatonin and curcumin.
Specifically, When Do Antioxidants Act?
Antioxidants provides different aid, at different stages of the oxidation process:
- Protect the cells from oxidation process, at different stages of the oxidation process:
>
Before
the oxidation process can damage the cells (Level 1)
>
After
the oxidation process already started, they can arrest the damage by either
eliminating the Free Radicals or neutralizing the Free Radicals, and repairing whatever damages done (Level 2)
- Repair the cells after the damage has been done (Level 3)
So, antioxidants have both a PREVENTION and CURE agenda.
Different Stages of Workings of Antioxidants
1st Level Defense
Protection BEFORE the damage can be done
This is the Preventative Way.
With sufficient levels of antioxidants in the body, free radicals have lesser chance of getting near the cells to cause damage. And if they do get to the cells, antioxidants can neutralize its damaging attacks before they can create any damage to the cells.
These antioxidants are usually the Enzymes antioxidants produced by the body, such as :
- Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- Catalase
- Glutathione Peroxidase
However, the cells also rely on "external" antioxidants from food, water and if need be, supplements, such as :
- Vitamin A, C and E
- Lycopene
- Minerals, such as Selenium
- Hydrogen
2nd Level Defense
Clean Up and Repair AFTER the damage assault
has begun
It’s still not too late if the damage attack on the cells has begun, antioxidants can still arrest the damage and carry out repairs, where required.
3rd Level, Repair
Repairing AFTER the damage - providing the Cure
When we do not have sufficient antioxidants in the body and when the damage has already been done, all is still not lost, as antioxidants have repair capabilities.
However, what
can be repaired is dictated by the body or cells, not by antioxidant. They want to
do their repair job but certain type of cells cannot be repaired. As we know
today, once brain cells are damaged, we can no longer repair them.
And some damages, if left for too long, may be beyond repair ...
As the old adage goes, “Prevention is BETTER than cure”, in which it would be best to ensure that we always have sufficient levels of antioxidants in the body.
Home > Return to the Top - What are Antioxidants?
Do you have a PASSION you want to share with the world??? What better exposure than the INTERNET?!!!
Want to consider?
Well, you will need a place to "host" (place) your site, then the tools to build, run as well as track the performance of your Masterpiece!
OR, if you already have a site, but find that you are paying too much for tools and apps to run and track your site ...
Here's an All-in-One Solution for you! Hosting, as well as Tools to build, run and track!
